Abstract
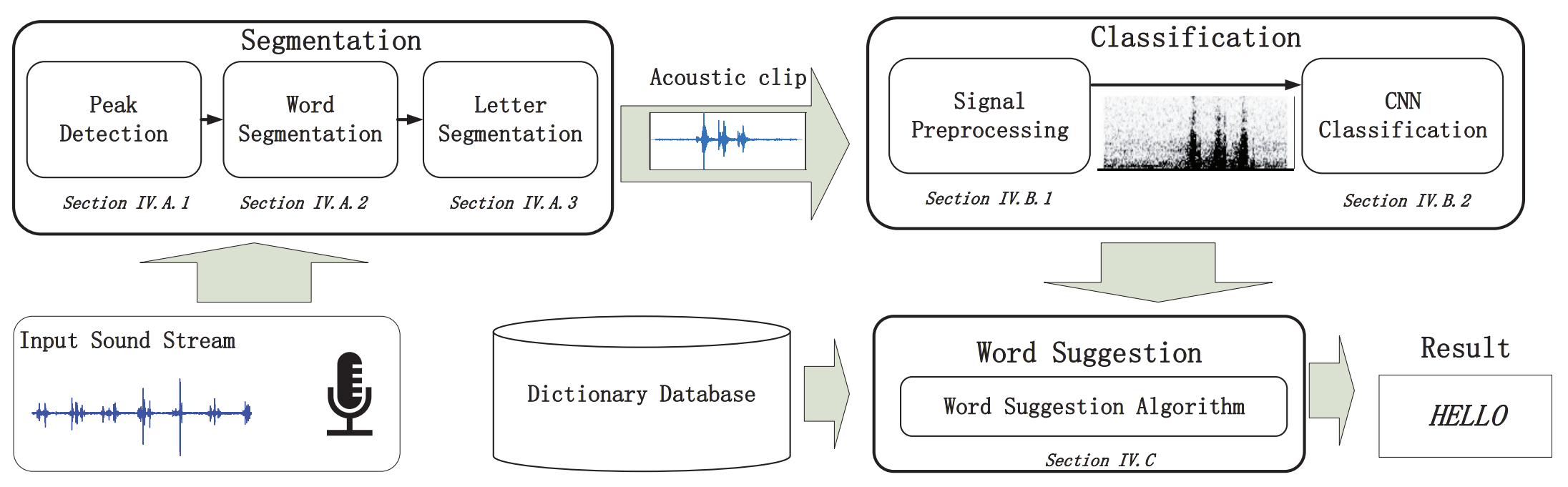
This paper presents WordRecorder, an efficient and accurate handwriting recognition system that identifies words using acoustic signals generated by pens and paper, thus enabling ubiquitous handwriting recognition. To achieve this, we carefully craft a new deep-learning based acoustic sensing framework with three major components, i.e., segmentation, classification, and word suggestion. First, we design a dual-window approach to segment the raw acoustic signal into a series of words and letters by exploiting subtle acoustic signal features of handwriting. Then we integrate a set of simple yet effective signal processing techniques to further refine raw acoustic signals into normalized spectrograms which are suitable for deep-learning classification. After that, we customize a deep neural network that is suitable for smart devices. Finally, we incorporate a word suggestion module to enhance the recognition performance. Our framework achieves both computation efficiency and desirable classification accuracy simultaneously. We prototype our design using off-the-shelf smartwatches and conduct extensive evaluations. Our results demonstrate that WordRecorder robustly archives 81% accuracy rate for trained users, and 75% for users without training, across a range of different environment, users, and writing habits.
Author
Haishi Du; Ping Li; Hao Zhou; Wei Gong; Gan Luo; Panlong Yang
Publication
IEEE INFOCOM (CCF-A) [Link] [PDF]
Keywords
Acoustics , Handwriting recognition , Writing , Microsoft Windows , Feature extraction , Conferences , Machine learning